I. Introduction
The cannabis industry has experienced a significant increase in growth and innovation in recent years, with extraction techniques being a key driver of this evolution. These techniques are vital in maintaining the integrity of cannabinoids and terpenes, the compounds that give cannabis its medicinal and recreational properties.
Table of Contents
ToggleThis article compares two specific techniques: aerosol R-134a extraction and butane hydrocarbon extraction. Although both methods strive to extract these valuable compounds from the cannabis plant, they differ considerably in their processes, results, and environmental impacts. R-134a is an aerosol gas similar to CO2, while butane and hydrocarbons are liquid solvents, highlighting the industry’s diverse range of extraction solvents.
II. R-134a Extraction Technique
The R-134a extraction process is the perfect flavoring extraction process and is a cutting-edge approach to extracting essential oils and other sensitive nonpolar compounds from plant material. It employs R-134a, a hydrofluorocarbon in gas form, as a primary extraction media.
How does it work?
In the R-134a aerosol extraction method, the plant material is placed in an extraction vessel where R-134a is introduced under specific temperature and pressure conditions. This method uses lower pressure and temperature conditions to preserve all terpenes and vital ingredients. The R-134A aerosol attracts the desired compounds, separating the resulting extract from the plant material. The R-134a fully evaporates, leaving a highly concentrated extract of the desired compounds with no residues.
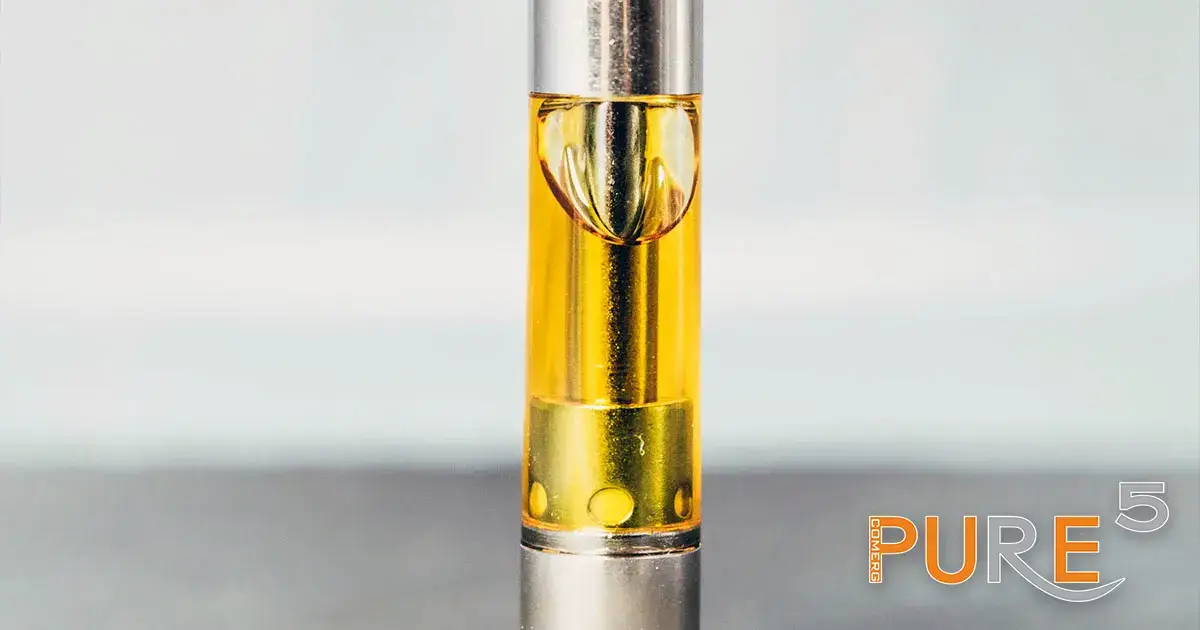
Pure R-134A Cannabis Extract
R134a as a solvent
One of the key benefits of the R-134a extraction method is its inert nature. The process is purely physical, attracting the active compounds through their electromagnetic properties, as the gas dielectric constant establishes the molecule’s polarity and not by chemical means. Unlike other extraction methods that leave residual solvents in the final product, the R-134a extraction ensures that no residual solvent remains under ambient conditions. This yields a more pure and much safer product.
R-134a is known for preserving extract integrity. It allows for the extraction of compounds without altering their natural state, ensuring that the integrity of the compounds is maintained. This is particularly important for preserving all the cannabinoids, terpenes, and vital ingredients intact, which means keeping their therapeutic and aromatic properties.
Efficiency and Extraction Quality of R134a Extraction
This extraction method results in a highly concentrated extract, ensuring the optimum potency of the finished product. This makes the method ideal for producing high-quality essential oils and other plant extracts.
When used in a proper automated extraction machine, such as those offered by PURE5™, R-134a is entirely safe. This method’s lower pressure and temperature requirements eliminate the need for extra training or permits, making it an accessible and user-friendly extraction technique.

Easy to use R-134A extraction equipment with automatic controls and intuitive settings.
III. Hydrocarbon Extraction
Hydrocarbon extraction is widely used to extract terpenes and other active compounds from plant material. This technique employs hydrocarbons, specifically butane, as a solvent.
How does it work?
The plant material is placed in an extraction vessel, and the hydrocarbon solvent is introduced under low temperature and moderate pressure conditions to maintain its liquid phase while touching the material. The cold state is required to limit the extraction of fats and lipids.
The solvent dissolves the desired compounds, separating the resulting solution from the plant material. Subsequently, the solvent is evaporated, leaving behind a highly concentrated extract of the desired compounds with slight traces of residual solvent remaining in the final extract. Because of the higher flammability, hydrocarbon extraction needs various permits, a particular C1D1 room setup, and meticulous staff training to maintain safety procedures.
Butane as a Solvent
In hydrocarbon extraction, butane is commonly used as a solvent due to its ability to dissolve organic compounds. However, it presents challenges. Despite its relatively low boiling point, making removal seem easy, it usually takes days to purge, and significant residues of these solvents persist in the final product.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness is debatable. While initially seeming economical, the expenses associated with safety measures and regulatory compliance are substantial. Specialized equipment, ventilation systems, and employee training are required to ensure safety. Moreover, stringent regulations demand costly purification processes to meet residual solvent limits in extracts.
Additionally, butane and propane are volatile organic compounds (VOCs) known to contribute to air pollution and climate change. Emissions during extraction pose health risks, necessitating strict emissions controls and environmental monitoring.
Efficiency and Extraction Quality of Hydrocarbon Extraction
The hydrocarbon extraction method is recognized for its efficiency and good quality. It is capable of extracting a wide range of compounds; however, residual solvents in the final extract may alter the compounds’ natural state. This results in a mid-quality extract maintaining most of the compounds’ original properties. Additionally, the method is efficient, yielding a high quantity of compounds from a given amount of plant material.
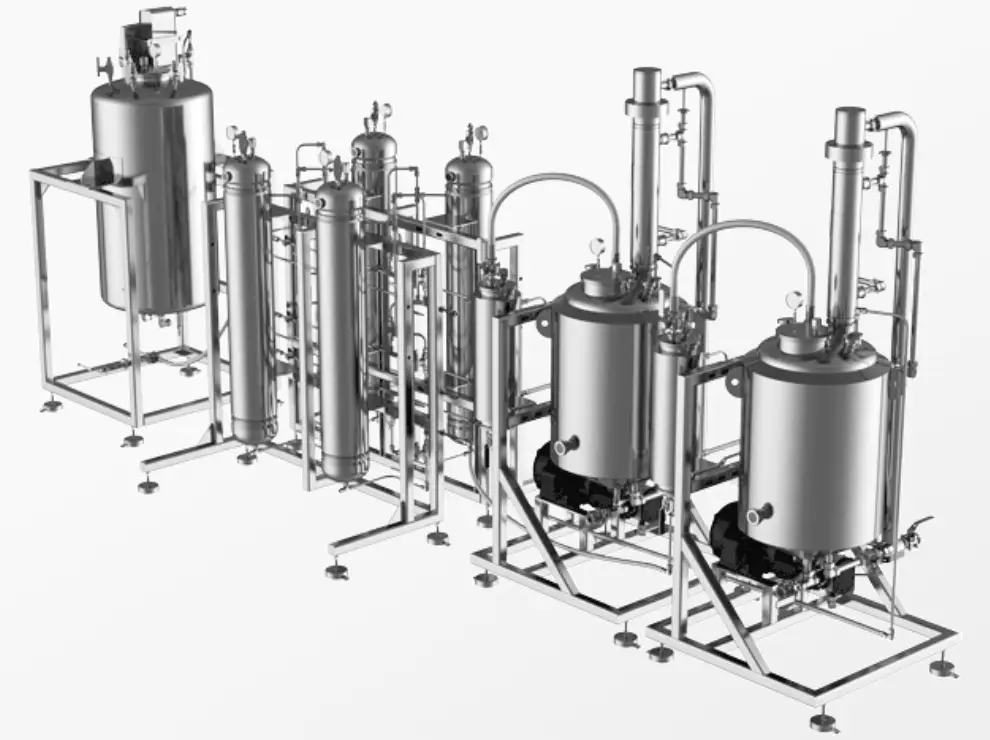

Visualization of BHO Hydrocarbon Cannabis Extractor
Hydrocarbon extraction is a robust technique for extracting plant oils and other compounds from plant material. Its advantages, such as efficiency and extraction quality, make it a choice for many.
Acknowledging the risks associated with hydrocarbon solvents, such as flammability, which requires careful management to ensure safe and effective extraction or the environmental impact and purification costs that make them less favorable options for cannabis extraction, is essential.
IV. Comparative Analysis
Preservation of Terpenes
Both R-134a and hydrocarbon extraction techniques can preserve terpenes. However, the R-134a extraction method stands out for its exceptional ability to retain sensitive cannabinoid and terpene characteristics, ensuring their therapeutic and aromatic properties are preserved.
While capable, the hydrocarbon extraction technique does not provide the taste compounds deriving from the flavonoids and is missing some small-molecule-weight terpene molecules, which makes it a lower-value extract for flower-experience replacement.
Removing of Residual Fillers
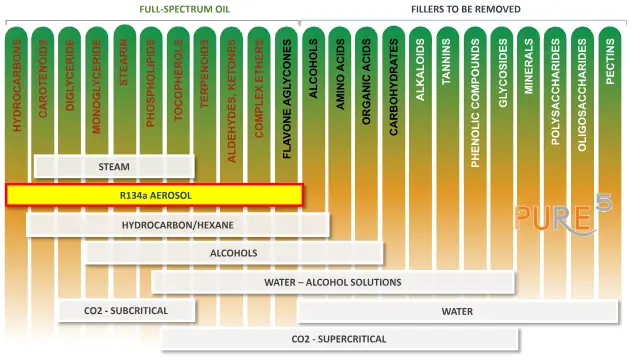
The comparison examines the necessity of removing residual fillers from plant extracts obtained through different extraction methodologies. R-134a aerosol extraction demonstrates a distinct advantage as it yields a full-spectrum oil without requiring additional removal of the fillers.
In contrast, hydrocarbon or hexane extraction and other conventional methods necessitate the extraction of residual fillers post-solvent evaporation. These residual fillers require additional steps and more complex systems, extending the extraction process and resulting in extra residual particles in the final extract.
Fillers needed to be removed during plant extraction
The comparative analysis highlights the efficiency of R-134a extraction over hydrocarbon extraction due to its inherent full-spectrum nature and simplified extraction process.
For more detailed information, refer to the accompanying image, which displays the composition of full-spectrum oils and associated fillers removed during extraction.
Cost-Effectiveness
When it comes to cost-effectiveness, the R-134a extraction technique is best. R-134a aerosol is cheaper and more readily available, especially considering long-term operational costs. Using closed-loop, fully automated extraction machines makes the R-134a technique more accessible and cost-effective. On the other hand, the hydrocarbon extraction technique can incur higher costs over time due to extract quality, safety, permits, worker training, healing potency of the plant’s oil, and environmental considerations.
With 2kW power and better than 99% recovery of the aerosol, running the fully automated aerosol extraction costs a few hundred dollars a month. The extraction is classified as nonvolatile, and there are no special requirements for environmental safety.
Safety Considerations
Safety is a paramount concern in extraction techniques. The R-134a extraction technique uses nonflammable media, which is much safer. It does not leave any residuals in the final product and can be evaporated entirely due to the low boiling point. This is a significant advantage over the hydrocarbon extraction technique, which uses highly combustible and flammable solvents and carries inherent safety risks.
Environmental Impact
The R-134a extraction technique is superior in terms of environmental impact. It uses a completely sealed system, preventing any release of R-134a into the environment. This starkly contrasts the hydrocarbon extraction technique, which has the potential for explosions if not properly managed.
The r-134a extraction technique outperforms the hydrocarbon extraction technique in terms of terpene preservation, cost-effectiveness, safety, and environmental impact. It uses cheaper, safer media and a fully automated extraction process, making it a better alternative for terpene extraction.

V. Conclusion
In conclusion, both R-134а and hydrocarbon extraction techniques offer unique advantages in extracting cannabinoids and terpenes from cannabis. R-134а, with its nonvolatile nature and ability to preserve the integrity of the extract, provides an exceptional solution for the medicinal and recreational markets, an alternative to traditional methods like hydrocarbon extraction. R-134a provides a cheaper, safer, and more environmentally friendly approach while ensuring high-quality results with intuitive ease of use.
The decision to use R-134a over hydrocarbon extraction depends on specific extraction requirements, desired final product characteristics, yield, cost, safety considerations, and environmental impact. As the cannabis industry continues to progress, R-134a extraction represents an exciting avenue for further innovation and development in cannabinoid and terpene extraction techniques, especially for new and growing businesses.
R-134а High Octane Full Spectrum Cannabis Extract