Introduction
For thousands of years, cannabis has been associated with relieving symptoms of disease and has demonstrated numerous therapeutic properties. In this century, we are finally beginning to understand the precise pharmacological mechanisms underlying the effects of cannabis and related preparations, most of which can be explained through the endocannabinoid system.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are natural plant compounds?
Cannabinoids
Many plants have been selectively bred to produce a maximum of THC and CBD, which is obtained by curing the flowers. Various compounds rich in cannabinoids, including hashish and hash oil, are extracted from the plant. Beside the cannabinoids there are a lot of beneficient plant compounds that are of high value as terpenes, flavonoids and carotenoids.
THC
THC is the component in cannabis responsible for the plant’s psychoactive effects. THC is a cannabinoid that interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system by attaching to the CB2 cannabinoid receptor in the brain, which activates neurons that influence pleasure, memory, thinking, coordination, and time perception.
CBD
CBD is not intoxicating or psychoactive. It that interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system by attaching to the CB1 receptor Proponents of CBD oil and other CBD products claim that it can be used to treat conditions such as chronic pain, inflammation, migraines, epilepsy, autoimmune diseases, depression, and anxiety.
Cannabis Terpenoids
Terpenoids are aromatic compounds that fulfill unique ecological roles for plants in protection from predators, attracting of pollinators, and myriad other roles. They are typically produced in dedicated structures, which in the case of cannabis are the glandular trichomes, the same
β-Myrcene
β-Myrcene is the most prevalent terpene in modern cannabis chemovars in the United States and in Europe, and is likely most responsible for sedative effects of many of the common preparations in commerce. Myrcene is anti-inflammatory via prostaglandin E-2 (PGE-2), blocks carcinogenic effects of aflatoxin in the liver.
β-Caryophyllene
BCP, a bicyclic sesquiterpenes alkene, is the most common terpenoid in cannabis extracts, and is nearly ubiquitous in food in the food supply. BCP acts as a selective full agonist at CB2 with strong potency (100 nM), and its antiinflammatory effects are reduced in CB2 knockout mice.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids, including anthocyanins, have been reported to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Anthocyanins could potentially provide a wealth of benefits. They may play a role in protecting the heart and liver, improving vision, as well as helping to prevent obesity and diabetes.
Carotenoids
Carotenoids are another group of pigments that can influence the colors of marijuana. They are created by plants, algae, and photosynthetic bacteria. Beta-carotene, lycopene, lutein, and zeaxanthin are among the more than 750 carotenoids that have been identified.
What is RSO?
Rick Simpson Oil (RSO) is named after its creator, Rick Simpson, a Canadian man who claims to have used the oil to cure his skin cancer. In 2003, Simpson was diagnosed with skin cancer and began researching alternative treatments, he eventually discovered the potential health benefits of cannabis oil and began experimenting with different extraction methods to create his own.
He ended up applying RSO topically to the cancerous area, and covering it with a bandage. After several days, he removed the bandage to find that the cancerous bumps were gone. After his success story, Simpson began sharing his story and promoting RSO as a natural alternative to traditional cancer treatments. Since then, the oil has become known as Rick Simpson Oil.
RSO is a cannabis oil extracted from the buds of the cannabis plant using room temperature ethanol. RSO is often touted as a potent and natural alternative to traditional cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy. However, the scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited, and RSO has not been approved by the FDA or any other regulatory agency to treat cancer or any other medical condition.
What is GSO?
George Stantchev Oil (GSO) is named after the inventor of the aerosol extraction technology that is producing the high quality Hash Resin extract. The oil is extracted under room temperature conditions using pharmaceutical level aerosol gas. The oils extracted are naturally pure and resemble the complete strain profile of the cannabis plant.
The complete full body of the terpenes is extracted in the front which is the absolutely complete terpene profile of the strain that recreates the complete flower experience. The cannabinoids are cured and extracted on the backend and enriched with the frontend terpenes.
The GSO oils maintain the original PH and enzymatic content of the flower which guarantees the natural plant potency and performance. The use of GSO enables reducing the THC dose in some treatments, and as a result, potentially minimizing the THC-related adverse effects. This would also help in adjusting the treatment to more sensitive populations such as children and elderly.
The latest studies show that the best combination of terpene and cannabinoid mixtures are formed by the natural strain plant profile and those should be maintained through the entire process including extraction for best medical results. Further GSO extracts maintained the antioxidant activity high above 80%.
What is the Pharmacology of GSO Hash Resin?
Over the past years, several lines of evidence support the therapeutic potential of Cannabis derivatives and in particular phytocannabinoids. Δ9-THC and CBD are the most abundant phytocannabinoids in Cannabis plants and therapeutic applications for both compounds have been suggested in the treatment of multiple cancer and mental illnesses.
However, CBD is recently emerging as a therapeutic agent in numerous pathological conditions without the psychoactive side effects exhibited by Δ9-THC. It is known that cannabinoids produce effects on some cancer-associated symptoms such as bone pain.
Below we performed a study with GSO Hash Resin in 2016 by the Medical University of Sofia, Faculty of Pharmacy, Sofia, Bulgaria, Institute of Microbiology, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Sofia, Bulgaria and National Hematological Hospital, Sofia, Bulgaria.
Since our Hash Resin is a well tolerated fully natural compound that mitigates the typical toxic effects of conventional chemotherapies, there is considerable merit in the development of cannabidiol as potential anticancer therapy for lymphoid neoplasms such as MM and CTCL.
The most sensitive cell line towards cannabidiol is RPMI-8226, followed by MJ and U-266.
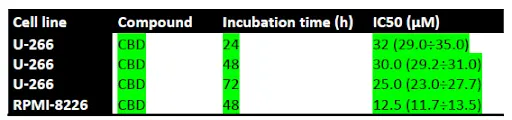
Concentration response curves showed IC50 values below 30 µM in all tumor cell lines investigated. Proteome analysis performed indicated up-regulation of pro-apoptotic signaling molecules such as Bad, Bax, caspase 3, cytochrome c etc., as well as down-regulation of anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2, HSP-70, clusterin etc. Nuclear fragmentation and cell cycle changes were demonstrated by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry.
Cancer results when cells grow faster and live longer than normal. Therefore increased activity of antiapoptotic proteins or decreased activity of proapoptotic proteins can contribute to the development of cancer. Below we show how GSO affects the antiapoptotic and pro-apoptotic proteins in the body after 48h treatment.
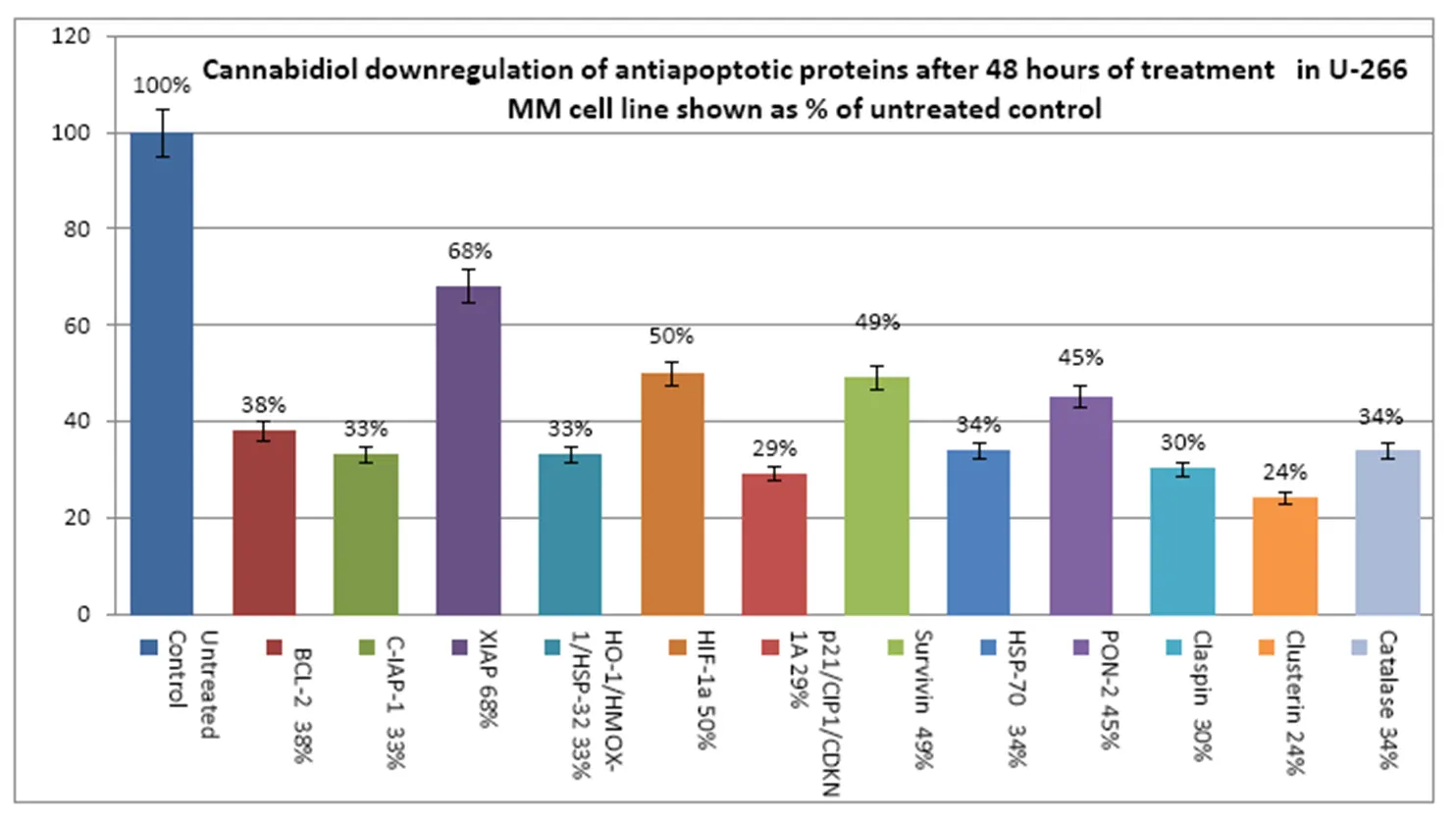
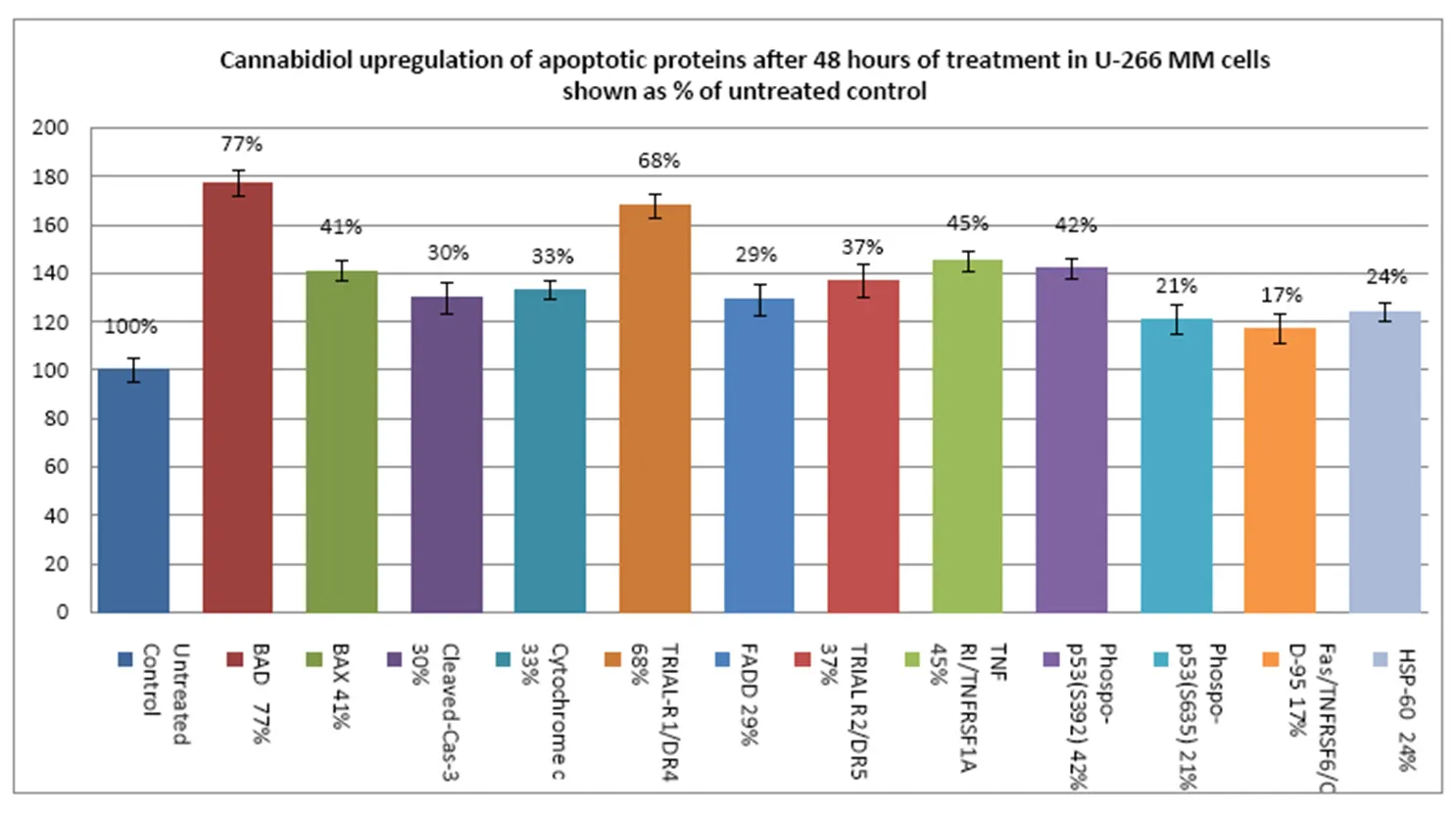
It is shown that the GSO extract has anti-myeloma activity. Since it is usually well tolerated and does not produce the typical toxic effects of conventional chemotherapies, there is considerable merit in the development of GSO as potential anticancer therapy for lymphoid neoplasms such as MM and CTCL.
GSO vs. RSO?
The origin and use of RSO dates back to 2003 when neither the legality of cannabis was clear nor the manners of obtaining cannabis oil were limited. At the time RSO was extracted with warm alcohol in a rice cooker, then ethanol evacuated by continuous boiling. The RSO obtained contained the major cannabinoids, wax, lipids and chlorophylls as a mixture. In later days the extraction was modified into cryogenic to limit the extraction of other compounds but the cannabinoids which degraded significantly the medical properties of the oil.
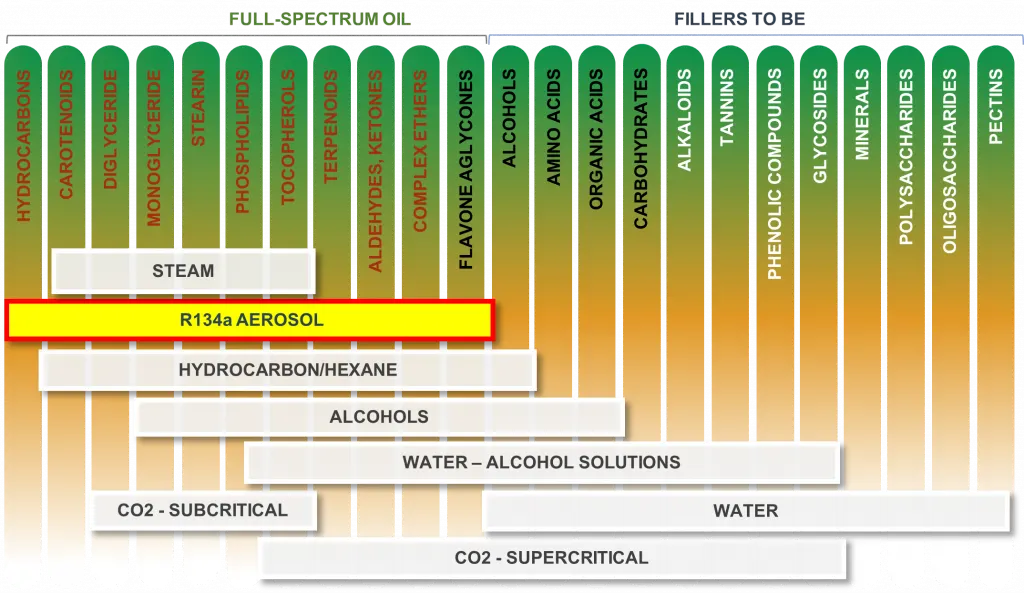
The GSO equipment was developed in the late 1990s and promoted for extraction in 2002 by COMERG, an European company initially in flavoring and fragrance extraction. The oils extracted with the method contain the complete terpene profile, ketones, ethers, flavones, carotenoids and cannabinoids. Due to no oxidation the extracts maintain the natural PH of the plant which is slightly alkaline in order to maintain medicinal properties. The original antibacterial values are preserved along with the extremely high antioxidant activity.
In addition the full body terpene profile activates the CB2 receptors before the cannabinoid bonds to it. Each terpene has different activating factors varying from 5% to 50%. This effect increases the bioavailability of the cannabinoids in times without the need of using activators and other chemical compounds in the extract.
Conclusion
As we see from the provided clinical sturdy Cannabidiol in the GSO Hash Resin downregulates anti apoptotic factors and upregulates the expression of pro apoptotic proteins which are involved in both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of programmed cell death. The terpene profile in the GSO improves the THC metabolization in human cells activating the CB1 receptors and minimizing the THC dose in delivery with about 50%.








