А method of extraction that involves keeping a plant in contact with a liquid (solvent) for a while.
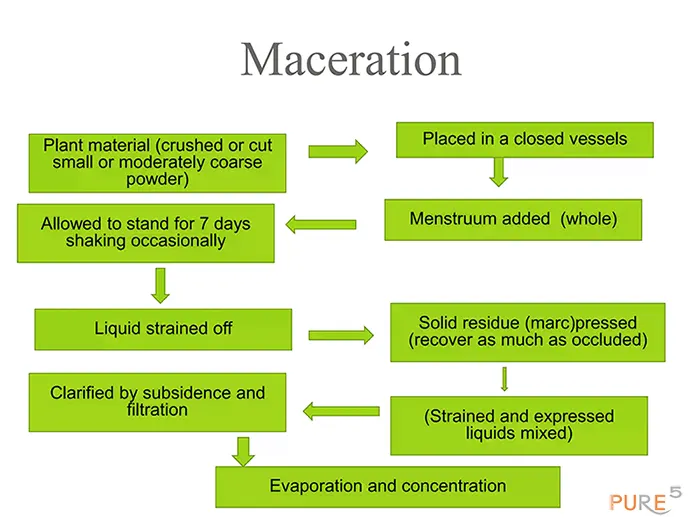
A botanical extraction method called maceration is carried out at room temperature. It entails submerging a plant for a variable amount of time, depending on the plant material and liquid employed, in a liquid (such as water, oil, alcohol, etc.) inside an airtight container.
The plant needs to be thoroughly cleaned and freed of impurities like soils, stones or boulders, weeds, and components unsuitable for extraction before processing. Depending on the desired outcome, the plant material can be employed either fresh or dry.
The material also must be sliced into small pieces in order to improve contact between the plant material being extracted and the liquid (solvent).
In order for the solvent to reach the deepest cells, the fragments shouldn’t be too large. Additionally, they shouldn’t be ground into a powder because doing so would destroy the plant’s volatile active compounds (essential oils), as well as make it more difficult to separate the plant material from the liquid utilized after maceration.
Based on the chemical makeup of the chemicals present in the plant, the solvent must be selected. The solvent should be chosen based on its solubility and the intended use of the extraction. Specifically, understanding their solubility and the intended application of the extraction. Alcohol is typically the chemical that is utilized the most since it can extract a larger portion of the molecules (active components) present in the plant, including molecules that are hydrophilic, or soluble in water, or lipophilic, or soluble in oil or other organic solvents.
To separate only the lipophilic (fat-containing) components, one uses a vegetable oil, whereas to remove only the hydrophilic (water-containing) components, one uses water.
Plant extracts that are available through maceration include:
Infusion in which the plant, whether it is fresh or dried, is allowed to macerate in a vegetable oil. A plant, either fresh or dried, is allowed to macerate in vegetable oil.
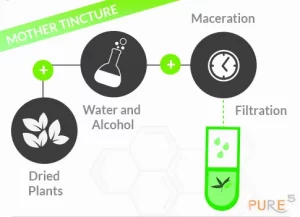
Glyceric Macerates: This substance is a blend of ethyl alcohol, water, and glycerin in equal parts. The plant elements that are often macerated in this combination include embryonic tissues like buds and immature sprouts.
Glycolic extracts are made after the plant has been macerated in propylene glycol. Only use this solvent externally.
The glycolic extracts and the infusion should only be applied externally. Instead, tinctures, mother tinctures, and macerated glycerides have internal and exterior applications.
Only external use is advised for the infusion and glycolic extracts. Instead, macerated glycerides, mother tinctures, and tinctures have both internal and external uses.
It is advisable to mix the plant inside the container at least once a day throughout the maceration process to make sure the solvent absorbs all of the plant material.
For your extraction needs – take a look at PURE5™’s equipment below: